-->
The actual startup folder locations vary, depending on which version of Excel you use. Folders that Excel uses at startup. If you install Excel in the default location, Excel opens files from the following paths: In Microsoft Office Excel 2003, the path is C: Program Files Microsoft Office Office11 Xlstart. Mar 06, 2017 How to Change the Outlook Startup Folder Lori Kaufman @howtogeek March 6, 2017, 10:24am EDT By default, when you start Outlook, the inbox of the first email account you added is automatically opened.
Note
Office 365 ProPlus is being renamed to Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise. For more information about this change, read this blog post.
For a Microsoft Excel 2001 for Mac version of this article, see 259921.
Summary
This step-by-step article describes how to use the Microsoft Excel startup folders. Excel uses startup folders in two ways:
- To load Excel workbooks at startup.
- As a reference location for templates.
The actual startup folder locations vary, depending on which version of Excel you use.
Folders that Excel uses at startup
Windows 10 Start Menu Folder
If you install Excel in the default location, Excel opens files from the following paths:
In Microsoft Office Excel 2003, the path is C:Program FilesMicrosoft OfficeOffice11Xlstart
In Microsoft Office Excel 2007, the path is C:Program FilesMicrosoft OfficeOffice12Xlstart
C:Documents and SettingsUser_nameApplication DataMicrosoftExcelXLSTART
In this path, User_name is your logon user name.
The folder that is specified in the At startup, open all files in box.
Note
To find the At startup, open all files in box in Excel 2003, click Options on the Toolsmenu, and then click the General tab.
To find the At startup, open all files in box in Excel 2007, click the Microsoft Office Button, click Excel Options, and then click Advanced. The At startup, open all files in box is under General.
Accepted file types during Excel startup
You typically use startup folders to load Excel templates and add-ins. You can also use startup folders to load workbooks. When you load the following types of files from a startup folder, the files have the important characteristics that are described in the following list.
Templates
If you save a workbook named Book.xlt, and then put it in a startup folder location, that workbook is the default workbook when you start Excel or open a new workbook.
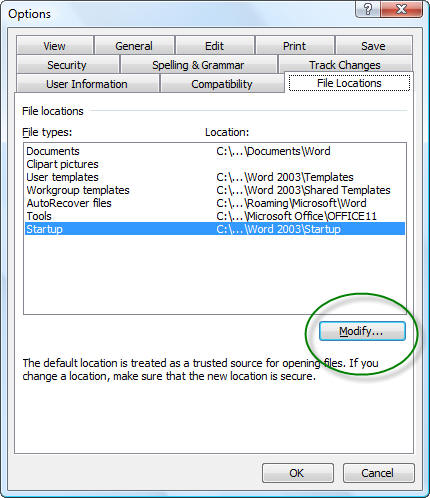
To use additional templates, you must save them in the following folder:
C:Program FilesMicrosoft OfficeTemplates1033
To use the templates in Excel 2003, follow these steps:
- On the Filemenu, click New.
- In the New Workbook task pane, click On my computer under Templates.
- In the Templates dialog box, double-click the template for the type of workbook that you want to create on the Spreadsheet Solutions tab.
To use the templates in Excel 2007, follow these steps:
- Click the Microsoft Office Button, and then click New.
- Under Templates, click Installed Templates.
- Under Installed Templates, click the template that you want, and then click Create.
Add-ins
Add-ins (.xla files) that you put in a startup folder do not typically appear when you start Excel. The add-ins are loaded in memory. The add-ins run any auto macros.
You can use these add-ins by whatever method the add-in provides (for example, a command on a menu or a button on a toolbar).
Workbooks
Workbooks (.xls files) that you put in a startup folder are loaded and appear when you start Excel, unless the workbook is saved in a hidden state.
For example, the personal macro workbook Personal.xls is a global macro workbook that Excel typically loads from the XLStart folder in a hidden state.
Incorrect use of the alternative startup file location
When you use the alternative startup file location, you must specify a file path where there are recognizable file types (such as templates, add-ins, and workbooks).
If Excel finds unrecognizable file types in a startup folder, you may receive an error message. The most common error message is:
This file is not a recognizable format.
Use the default file location
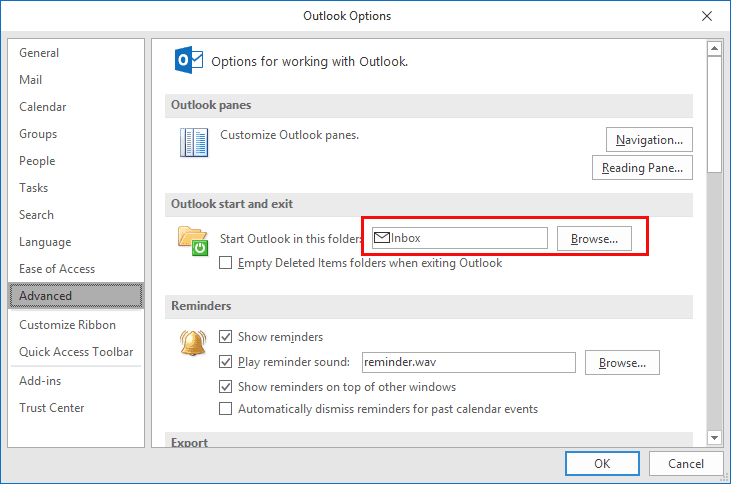
In addition to the alternative startup file location, the default file location can be set by using the Default file location box on the General tab in the Options dialog box in Excel 2003.
The default file location differs from a startup folder. It can set the folder location that you want Excel to point to when you open or save a file by using the File menu.
Note
In Excel 2007, to see the default file location, follow these steps:
- Click the Microsoft Office Button, and then click Excel Options.
- Click Save.
- The Default file location box is under Save workbooks.
To use any of these key combinations, press and hold the keys immediately after pressing the power button to turn on your Mac, or after your Mac begins to restart. Keep holding until the described behavior occurs.
- Command (⌘)-R: Start up from the built-in macOS Recovery system. Or use Option-Command-R or Shift-Option-Command-R to start up from macOS Recovery over the Internet. macOS Recovery installs different versions of macOS, depending on the key combination you use while starting up. If your Mac is using a firmware password, you're prompted to enter the password.
- Option (⌥) or Alt: Start up to Startup Manager, which allows you to choose other available startup disks or volumes. If your Mac is using a firmware password, you're prompted to enter the password.
- Option-Command-P-R:Reset NVRAM or PRAM. If your Mac is using a firmware password, it ignores this key combination or starts up from macOS Recovery.
- Shift (⇧): Start up in safe mode. Disabled when using a firmware password.
- D: Start up to the Apple Diagnostics utility. Or use Option-Dto start up to this utility over the Internet. Disabled when using a firmware password.
- N: Start up from a NetBoot server, if your Mac supports network startup volumes. To use the default boot image on the server, hold down Option-N instead. Disabled when using a firmware password.
- Command-S: Start up in single-user mode. Disabled in macOS Mojave or later, or when using a firmware password.
- T: Start up in target disk mode. Disabled when using a firmware password.
- Command-V: Start up in verbose mode. Disabled when using a firmware password.
- Eject (⏏) or F12 or mouse button or trackpad button: Eject removable media, such as an optical disc. Disabled when using a firmware password.
Windows 10 Startup Programs
If a key combination doesn't work
If a key combination doesn't work at startup, one of these these solutions might help:
- Be sure to press and hold all keys in the combination together, not one at a time.
- Shut down your Mac. Then press the power button to turn on your Mac. Then press and hold the keys as your Mac starts up.
- Wait a few seconds before pressing the keys, to give your Mac more time to recognize the keyboard as it starts up. Some keyboards have a light that flashes briefly at startup, indicating that the keyboard is recognized and ready for use.
- If you're using a wireless keyboard, plug it into your Mac, if possible. Or use your built-in keyboard or a wired keyboard. If you're using a keyboard made for a PC, such as a keyboard with a Windows logo, try a keyboard made for Mac.
- If you're using Boot Camp to start up from Microsoft Windows, set Startup Disk preferences to start up from macOS instead. Then shut down or restart and try again.
Remember that some key combinations are disabled when your Mac is using a firmware password.
Learn more
Office 365 Mac Student
- Learn what to do if your Mac doesn't turn on.
- Learn about Mac keyboard shortcuts that you can use after your Mac has started up.



